Administration of Herceptin SC into the Abdominal Wall
This article responds to your request for information on administration of Herceptin SC ® (trastuzumab and hyaluronidase) into the abdominal wall.
This response was developed according to principles of evidence-based medicine and contains data from a Phase 3 study.
Last updated March 27, 2025
Summary
- Herceptin SC is administered into the thigh by SC injection.
- The GAIN-2 substudy evaluated the PK, patient preference, and safety of Herceptin SC administered into the thigh versus the abdominal wall.
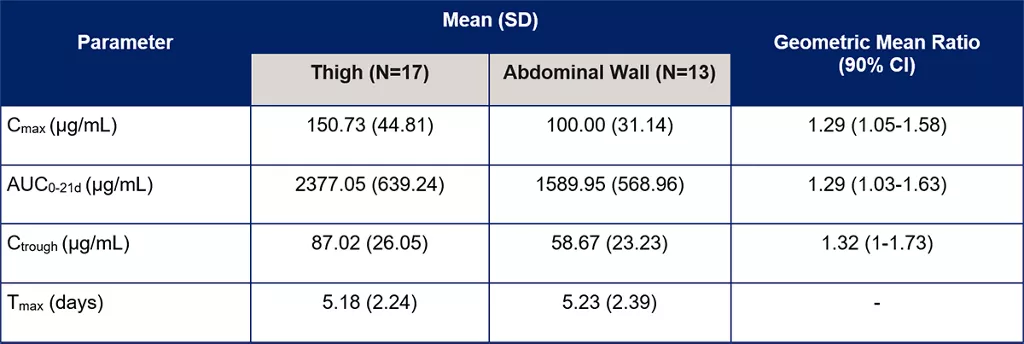
- Bioavailability was approximately 30% higher following SC administration into the thigh compared to the abdominal wall.
- Any grade and grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs were comparable between the two administration sites.
Abbreviations
AE=adverse event
AUC0-21d=area under the plasma-concentration time curve from 0-21 days
CI=confidence interval
Cmax=peak plasma concentration
Ctrough=trough plasma concentration
mITT=modified intention-to-treat
PK=pharmacokinetics
SC=subcutaneous
SD=standard deviation
Tmax=time to peak drug concentration
Recommended administration of Herceptin SC
Herceptin SC is a formulation of trastuzumab and recombinant human hyaluronidase, which is administered by SC injection into the thigh.[1] Recombinant human hyaluronidase is an enzyme that increases the dispersion and absorption of co-administered drugs when administered subcutaneously.[2]
GAIN-2 substudy evaluating administration of Herceptin SC into the abdominal wall
A substudy of the multicentre, randomised, Phase 3 GAIN-2 study evaluated the PK, safety, and patient preference of Herceptin SC when administered into the thigh versus the abdominal wall.[3] The mITT group included 219 patients, 110 in the thigh group and 109 in the abdominal wall group.
PK results comparing administration in the thigh to the abdominal wall
PK details were assessed in a pre-determined subset of 30 patients: 17 in the thigh group and 13 in the abdominal wall group.[3] Bioavailability was found to be approximately 30% higher following SC administration into the thigh compared to the abdominal wall.
Variability for Cmax, AUC0-21d, and Ctrough was also higher following administration into the abdominal wall than into the thigh.[3] Tmax was not significantly different between the two groups.
Figure 1 depicts the difference in mean plasma concentration over time between the two administration locations. A summary of various PK parameters is presented in Table 1.
Figure 1. Mean plasma concentration-time profiles of Herceptin SC administered into the thigh and abdominal wall [3]
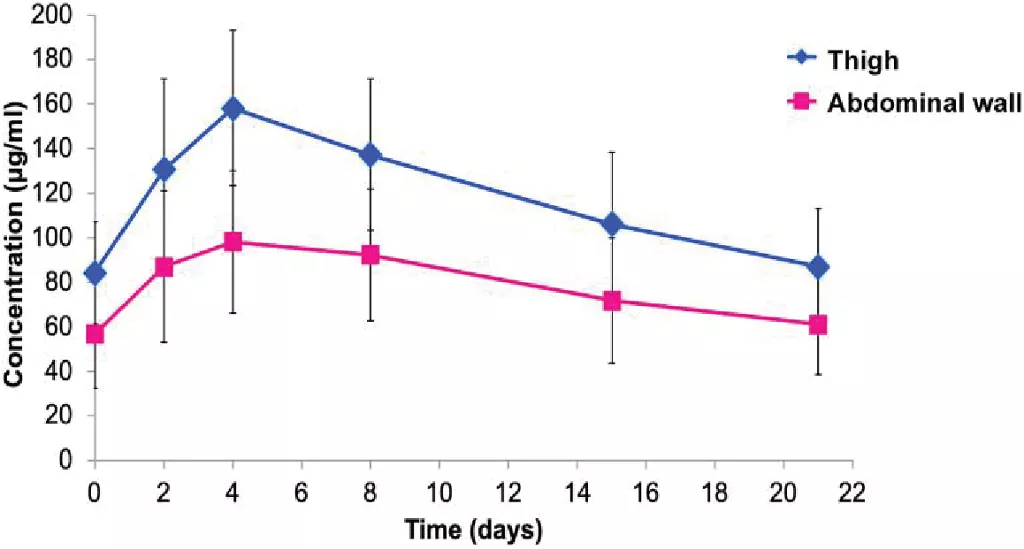
Table 1. Comparison of PK parameters for the thigh group compared to the abdominal wall group [3]
Safety results for the mITT group
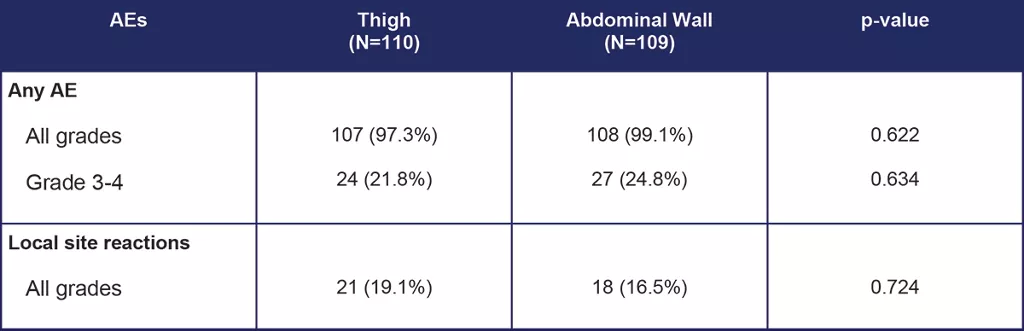
Safety was evaluated in the 219 patients in the mITT group.[3] Pain (p=0.01) and irritation around the injection site (p=0.033) was more commonly reported in patient interviews in the thigh group compared to the abdominal wall group.
The number of patients experiencing any grade and grade 3-4 treatment related AEs was comparable between injection sites.[3] The number of local site reactions did not differ significantly between sites.
Table 2. Summary of safety results for the mITT group [3]
References
- Ismael G, Hegg R, Muehlbauer S, et al. Subcutaneous versus intravenous administration of (neo)adjuvant trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive, clinical stage I-III breast cancer (HannaH study): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:869-78. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22884505
- Roche Internal Regulatory Report (Herceptin CDS v.21). Accessed 1 Sep 23.
- Reinisch M, Untch M, Mahlberg R, et al. Subcutaneous injection of trastuzumab into the thigh versus abdominal wall in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: Pharmacokinetic, safety and patients' preference - Substudy of the randomised phase III GAIN-2 study. Breast 2022;66:110-117. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36223695
Medinfo
Need to contact Roche?
Request Product Information
Request Product Information
Ask us a question and request information about Roche products or services.
Report a potential side effect
Report a potential side effect
If you have experienced potential side effects with a Roche product you can report it here.
Report a potential product defect
Report a potential product defect
If you suspect a potential defect or a Roche product has not met your expectations you can report it here.
Request temperature stability assessment
Request temperature stability assessment
Request an assessment if your product was stored outside the recommended temperature range.
