
Treatment
Disease classification determines therapy
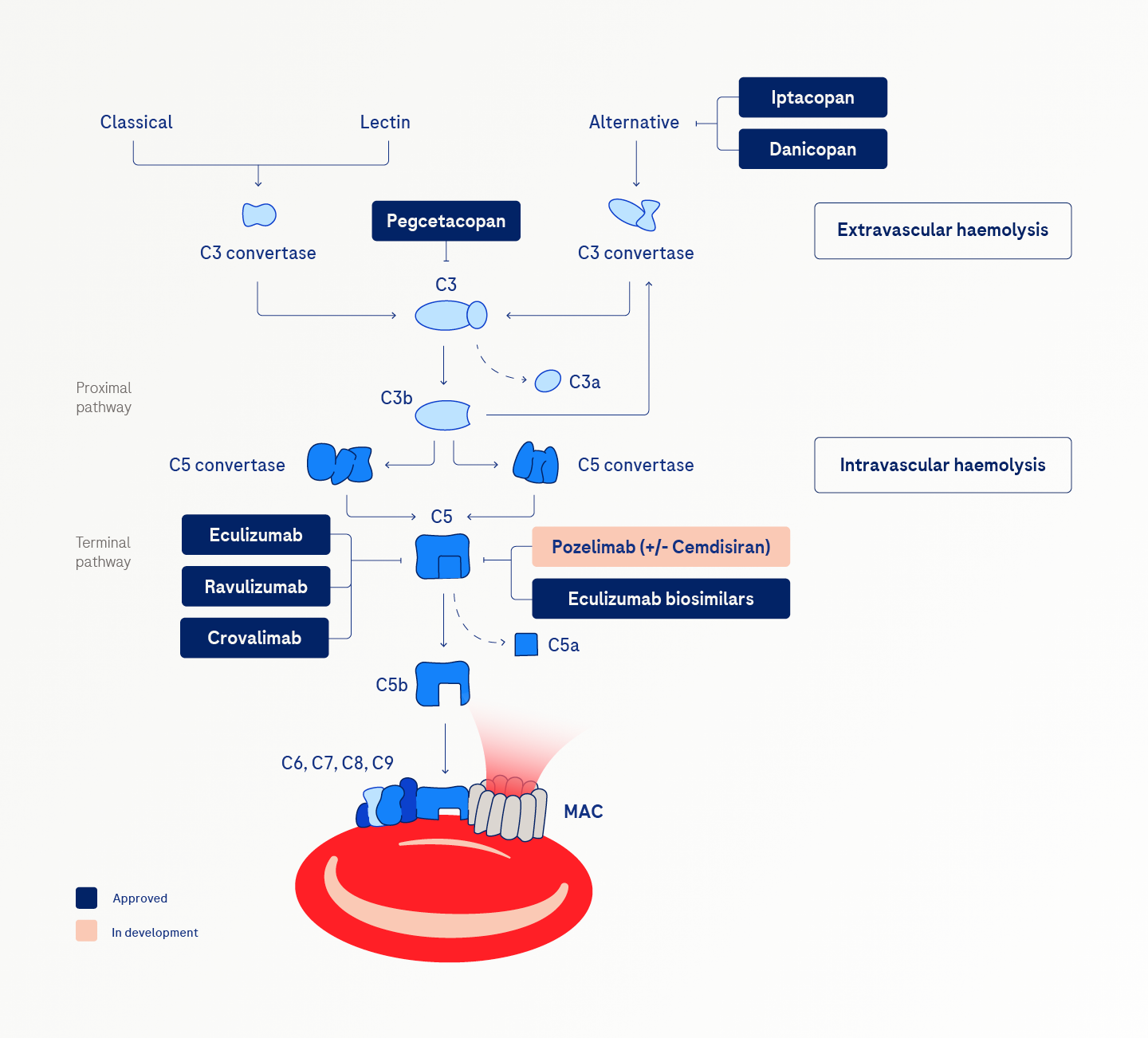
People with subclinical PNH require no specific treatment. For people with PNH associated with another bone marrow failure, therapy should primarily target the underlying syndrome. For people with classic PNH, complement inhibitors are utilised in regions where they are accessible.1
C5 inhibitors
C5 inhibitors bind to the C5 fragment and inhibit its cleavage to prevent membrane attack complex (MAC) formation, allowing PNH red blood cells to avoid complement-mediated lysis. These inhibitors effectively reduce excess haemolysis and thrombotic complications and significantly extend survival.2
Treatment with complement inhibitors can cause life-threatening infections with N. meningitidis and other encapsulated organisms. Meningococcal vaccination is mandatory before treatment initiation with C5 inhibitors.1,3
Other complement inhibitors
Proximal complement inhibitors target proteins upstream in the complement pathway, such as C3 and Factor B. They can address the needs of people with notable extravascular haemolysis.4,5
Unmet needs with current treatments
Despite the clinical benefits, breakthrough haemolysis may occur in patients with PNH due to incomplete complement inhibition.
The frequent dosing schedules and the need for intravenous infusions associated with current complement inhibitors contribute to a considerable treatment burden for people with PNH.2,4,6,7
While current complement inhibitors have transformed PNH treatment, challenges such as treatment burden, accessibility issues and genetic variations persist. Ongoing research into new therapeutic options with reduced burden and improved efficacy remains crucial in addressing the unmet needs of individuals living with PNH.
Existing unmet needs in PNH
Sufficient complement inhibition with no breakthrough haemolysis
Greater treatment convenience /reduced treatment burden
Effective treatment for patients with C5 SNP R885H for whom approved C5 inhibitors are ineffective
Increased access to effective treatments for all patients
Explore other PNH resources
References:
- Parker CJ. Update on the diagnosis and management of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016; 2016 (1): 208–216. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.208
- Risitano AM, Marotta S, Ricci P et al. Anti-complement treatment for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: time for proximal complement inhibition? A position paper from the SAAWP of the EBMT. Front Immunol. 2019; 10: 1157. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01157
- Brodsky RA. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2014; 124 (18): 2804–2811. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-02-522128
- Nishimura J, Yamamoto M, Hayashi S et al. Genetic variants in C5 and poor response to eculizumab. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370 (7): 632–639. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1311084
- Kulasekararaj AG, Kuter DJ, Griffin M et al. Biomarkers and laboratory assessments for monitoring the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Differences between terminal and proximal complement inhibition. Blood Rev. 2023; 59: 101041. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2023.101041
- Lee JW, Sicre de Fontbrune F, Wong Lee Lee L et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in adult patients with PNH naive to complement inhibitors: the 301 study. Blood. 2019; 133 (6): 530–539. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-09-876136
- Panse J. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Where we stand. Am J Hematol. 2023; 98 (Suppl 4): S20–S32. doi:10.1002/ajh.26832
